You could change goods entries in "common.ini" to add the "a" on the end. This will affect all other displays of goods, such as in the store or in your hold. This might not be a bad thing since you usually have more than one of any item, so would the plural version be more correct everywhere?
I'm sorry I didn't explain correctly, I hope it makes more sense.
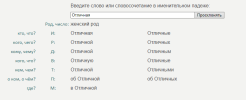
1) Nominative (И) (кто, что?). The noun before the predicate is the subject and is translated in the nominative case:
The student asked the teacher. - Студент спросил преподавателя.
2) Accusative (В) (кого, что?). The noun after the predicate is a direct object and is translated in the accusative case without a preposition:
The teacher asked the student. - Преподаватель спросил студента.
3) Dative (Д) (кому, чему?). A noun without a preposition, standing between a predicate and a direct object, is an indirect object and is translated in the dative case without a preposition:
The teacher showed the student a book. - Преподаватель показал студенту книгу.
Nouns with prepositions:
Nouns in the common case with prepositions express relations conveyed by Russian indirect cases without prepositions or with prepositions. For example:
4)Genitive (Р) (кого, чего?) - (of, from). The noun performs the function of determining the preceding noun:
He had received a letter from his girl-friend. - Он получил письмо от подруги.
Moreover, the preposition (of) expresses, most often, belonging, part of the whole, denotes the material or contents of the container of something:
The leg of the table is broken - Ножка стола сломана; the voice of the girl - голос девочки; a dress of blue silk - платье из голубого шелка; a bottle of milk - бутылка молока
3.1) Dative (Д) (кому, чему?) - (to, for). The noun performs the function of a prepositional indirect object:
I gave the ticket to my sister - Я отдал билет сестре; He bought a ball for his son - Он купил мяч сыну.
5)Ablative (Т) (кем, чем?) - (by, with). A noun with the preposition (by) performs the function of a prepositional complement, denoting the effective force after the verb in the passive voice:
America was discovered by Columbus - Америка была открыта Колумбом; by plane - самолетом.
The noun with the preposition (with) performs the function of a prepositional object, denoting the object with which the action is performed:
The child usually eats with this spoon - Ребенок обычно ест этой ложкой; to cut with a knife - резать ножом.
6)Prepositional (П) (о ком, о чем?) - (about, of). The noun performs the function of a prepositional indirect object:
They told us about the exhibition - Они рассказали нам об этой выставке; She spoke of literature and music - Она говорила о литературе и музыке.
In this case, 3.1 is suitable, since there is a preposition (to), but since it is a product, it is more appropriate to write here "Пороха, but not Пороху" - (Р) (кого, чего?) (whom, Because of which) Due to pitching, gunpowder was overboard.
Captain, the cargo has started shifting due to the rolling and 324 Gunpowder went overboard - Капитан, груз начал смещаться из-за качки и 324 Пороха оказалось за бортом.
So fixing everything in common.ini will not work, because there is a case: Nominative (И) (кто, что?)